Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song, or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution. This lesson covers the Cycles harmonic principle.



Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution.
This lesson covers the Cycles harmonic principle.
Available for Premium Site Access Plans Only

This series, is the book Harmonic Analysis for Chord Substitution and Scale Selection by Curt sheller broken out into individual lessons with additional examples and content. Always, the latest version of the book.
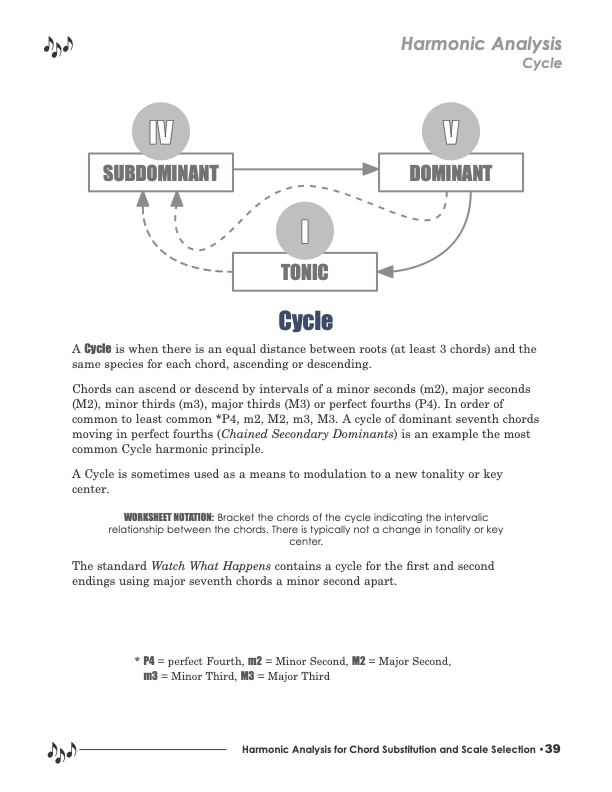
A Cycle is when there is an equal distance between roots (at least 3 chords) and the same species for each chord, ascending or descending.
Chords can ascend or descend by intervals of a minor seconds (m2), major seconds (M2), minor thirds (m3), major thirds (M3) or perfect fourths (P4). In order of common to least common *P4, m2, M2, m3, M3. A cycle of dominant seventh chords moving in perfect fourths (Chained Secondary Dominants) is an example the most common Cycle harmonic principle.
A Cycle is sometimes used as a means to modulation to a new tonality or key center.
WORKSHEET NOTATION: Bracket the chords of the cycle indicating the intervalic relationship between the chords. There is typically not a change in tonality or key center. m2 for Minor Second, M2 for Major Second, P4 for Perfect Fourth, P5 for Perfect Fifth, m3 for Minor Third, M3 for Major Third, etc…
The standard Watch What Happens contains a cycle for the first and second endings using major seventh chords a minor second apart.
Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution.
This lesson covers the Cycles harmonic principle.
Available for Premium Site Access Plans Only

This series, is the book Harmonic Analysis for Chord Substitution and Scale Selection by Curt sheller broken out into individual lessons with additional examples and content. Always, the latest version of the book.
A Cycle is when there is an equal distance between roots (at least 3 chords) and the same species for each chord, ascending or descending.
Chords can ascend or descend by intervals of a minor seconds (m2), major seconds (M2), minor thirds (m3), major thirds (M3) or perfect fourths (P4). In order of common to least common *P4, m2, M2, m3, M3. A cycle of dominant seventh chords moving in perfect fourths (Chained Secondary Dominants) is an example the most common Cycle harmonic principle.
A Cycle is sometimes used as a means to modulation to a new tonality or key center.
WORKSHEET NOTATION: Bracket the chords of the cycle indicating the intervalic relationship between the chords. There is typically not a change in tonality or key center. m2 for Minor Second, M2 for Major Second, P4 for Perfect Fourth, P5 for Perfect Fifth, m3 for Minor Third, M3 for Major Third, etc…
The standard Watch What Happens contains a cycle for the first and second endings using major seventh chords a minor second apart.
Harmonic Analysis - Cycles
Song Examples
Most folk, rock and blues songs remain in one key. Most Jazz and Pop standards will modulate to new key centers.
Jazz Classics
Watch What Happens
1st ending
Major 7 chords descending and ascending minor seconds (m2)
2nd ending
Major 7 chords ascending minor seconds (m2)
I Got Rhythm
Bridge
A cycle of Secondary Dominant chords with a distance of a Perfect Fourth (P4) between roots.
Jordu
Bridge
Contains two Secondary Dominant Seventh chord cycles
Stompin' at the Savoy
Bridge
Contains two Secondary Dominant Seventh chord cycles
Checkout the Songs section of LearningUkulele.com , as many of the songs examples above are available.
Related Lessons, Videos, Lesson Series, Songs, Books & Reference Charts, Resources & Assets, Workshops are below.

Harmonic Analysis ( HA ) is the process used to determine the harmonic function of chords within a chord progression. A chord progression is defined as a sequence of chords, each chord has a root and has a particular chord type. The relationship of a chord's root to a scale determines its function within that scale's tonality. Once a chord's function is identified, scale selections along with chord and scale substitutions can be made. This process is called Root Movement Analysis ( RMA ). This series of lessons are extracted from my book for use with individual private and on-line students. Each lesson directly corresponds the chapters in my book Harmonic Analysis for Scale Selection and Chord Substitution by Curt Sheller (me).

Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution.


return in your investment)—it is this— learning the
f*ckingnotes of your OWN instrument. Sorry for the tough talks—but it is sooooo true!


Learn to read single note melodies in the first/open position is a lot easier than you might think. Book: Ukulele – Reading Music Series – Primer

An organized collection of daily practice and reference material for the contemporary ukulele player for developing the vocabulary and knowledge necessary for single note playing. Book: Daily Practice Material for the Contemporary Ukulele
Checkout the Books & Reference Charts for additional Handy, Dandy Reference Charts.

Ukulele Fingerboard Chart for C Tuning, Low or High G – G C E A

Ukulele Fingerboard Chart for G Tuning, Low or High A – D G B E
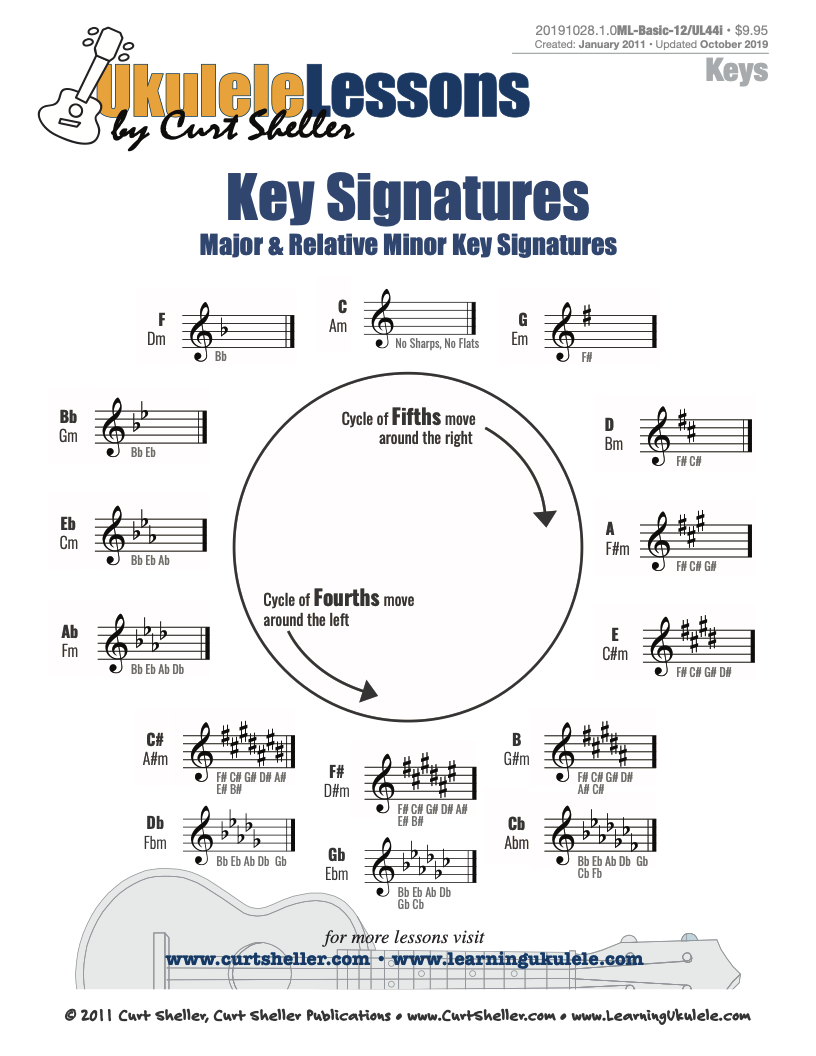
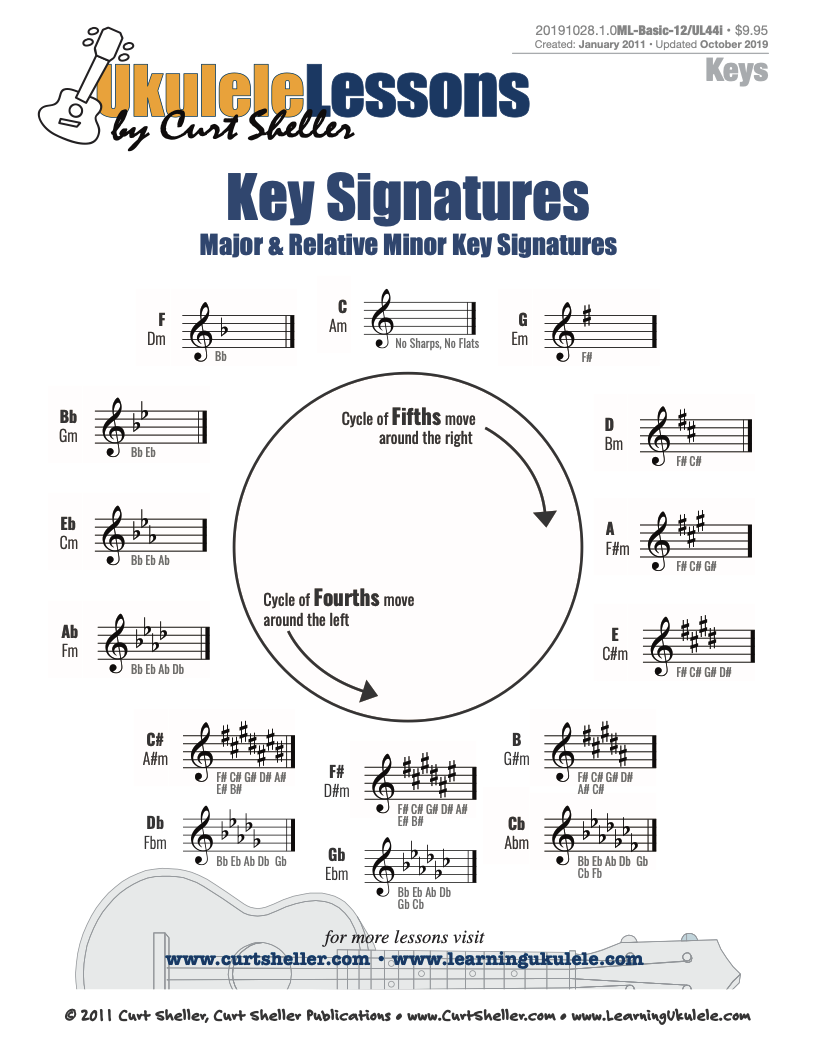
A handy reference chart of all 15 major and relative minor key signatures. US Letter 8.5 x 11 sized (ANSI-A) , A4








.jpg)