
An alternate approach to determining the chord tones of any chord. Bottom-line is, it's the notes that make the chord, not the shape. A C chord is C, E, G - NOT this or that shape.

Just what is "Up, Down, Ascending, Descending, Higher, Lower, Top, Bottom" as related to music?
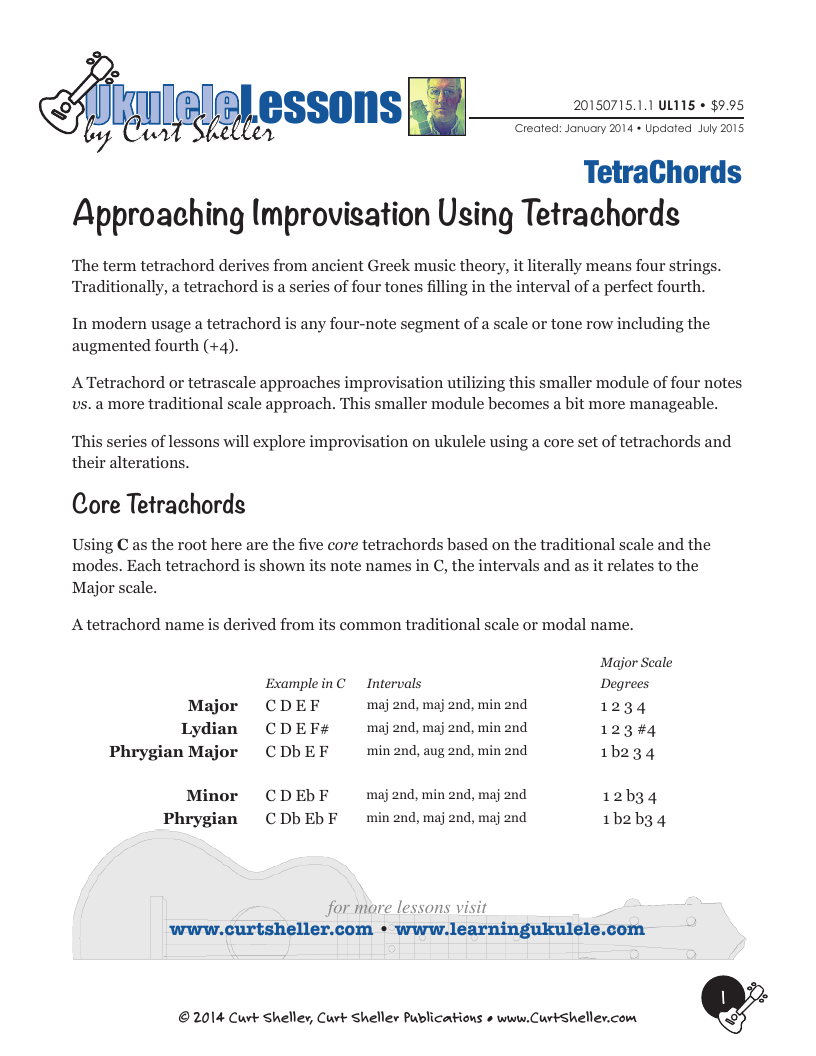
Traditionally, a "Tetrachord" is a series of four tones filling in the interval of a perfect fourth. In modern usage a tetrachord is any four-note segment of a scale or tone row including the augmented fourth (+4). The term tetrachord derives from ancient Greek music theory, it literally means four strings.**

An "Enharmonic Equivalent" is where a musical pitch can have different names depending on the context in which it is functioning. An example is G# produces the same pitch as Ab but have different standard notations when written in music.

The "Major Scale" or Ionian scale is a diatonic scale, made up of seven distinct notes, plus an eighth which duplicates the first one octave higher. In solfege these notes correspond to the syllables Do, Re, Mi, Fa, Sol, La, Ti/Si, (Do), the Do in the parenthesis at the end being the octave of the root.

Cut Time is a source of confusion for many musicians. What exactly does it mean and how do you apply it? Here is a guest lesson by internationally renowned jazz guitarist and educator Chuck Anderson.

Sequences and cycles for practicing scales, intervals, melodic sequences and arpeggios.

An interval is the distance between two notes. An interval has a name and a type. "Chromatic Intervals" are NOT taken from a major scale. They are derived from the diatonic intervals.
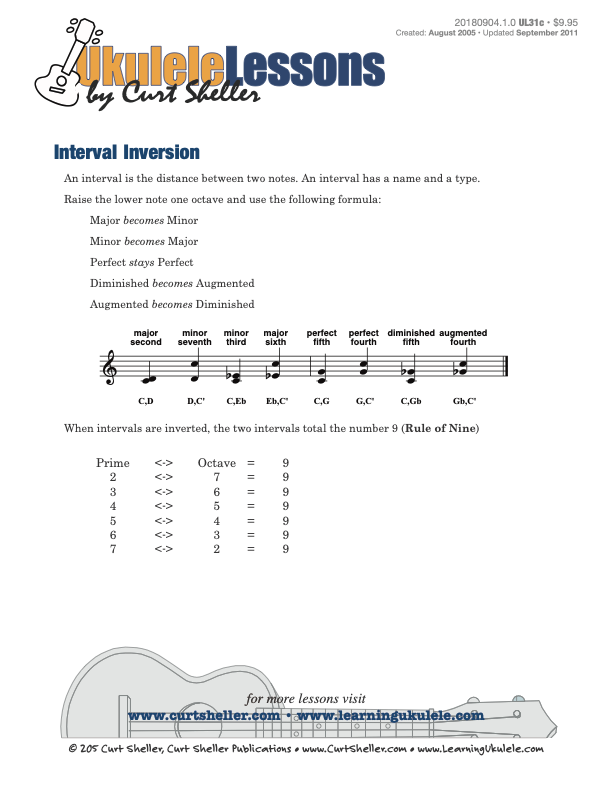
Inverting intervals using the "Rule of Nine". An interval is the distance between two notes. An interval has a name and a type. Intervals can be played one note (melodic) or two notes (harmonic) at a time, ascending or descending.
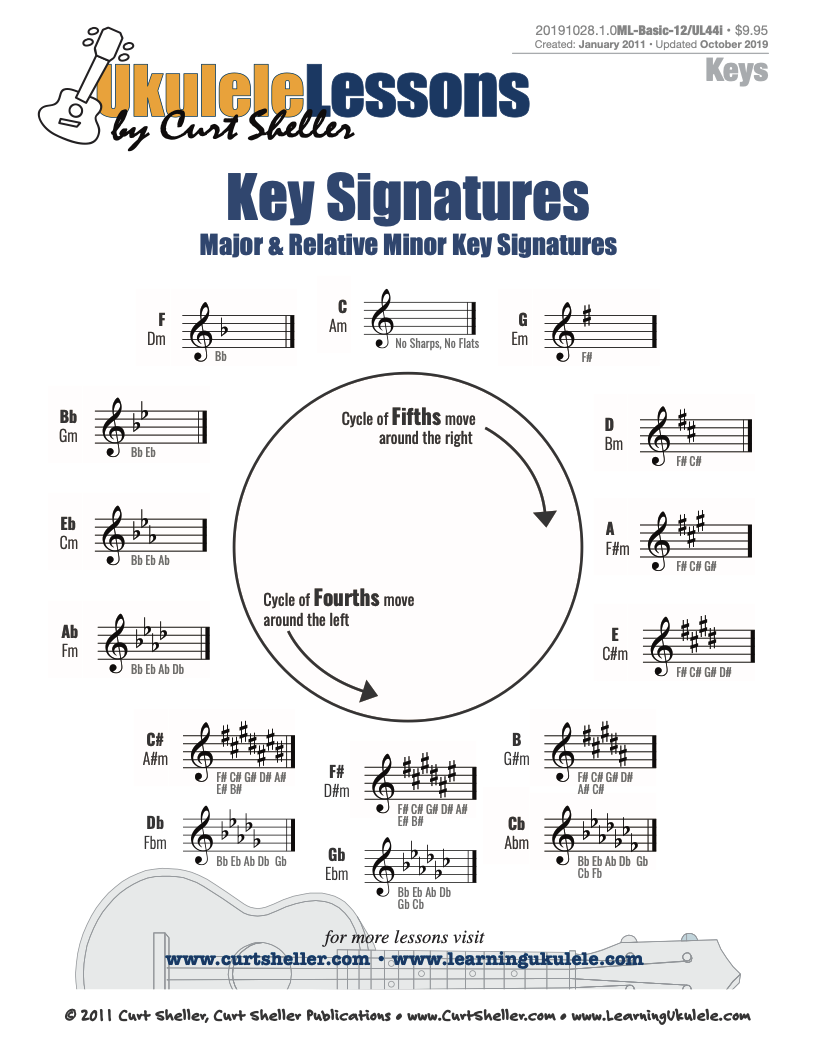
Traditional key signatures provide a wealth of information that can enhance our understanding of music and its underlying principles.

Ear Training is the development of the active and passive capability to relate to music aurally. This includes the ability to recognize melodic and harmonic intervals, chords, chord progressions, rhythm, melody, and harmony.

"D Major" (or the key of D) is a major scale based on D, with the pitches E F# G A B C#. Its key signature has two sharps: F# C#. Its Relative Minor scale is Bm Minor. Its Parallel Minor is D Minor.

"Cb Major" (or the key of Cb) is a major scale centered around Cb, with the following pitches: Cb, Db, Eb, Fb, Gb, Ab, and Bb. The key signature of Cb Major includes seven flats: Bb, Eb, Ab, Db, Gb, Cb, and Fb. The relative minor scale of Cb Major is Ab Minor, while the parallel minor is Cb Minor. Cb Major is considered relatively easy to memorize, as all of its notes are flat.

In music, it is important to learn and recognize the key signature for C Major and A Minor. These two keys have corresponding major and natural minor scales, along with basic ukulele chords that can be used with each scale. The key of C Major, also known as the learning key, is particularly easy to memorize and start using.

“G Major” (or the key of G) is a major scale based on G, with the pitches G A B C D E F#. Its key signature has one sharp: F#. Its Relative Minor scale is E Minor. Its Parallel Minor is D Minor.

"D Major" (or the key of D) is a major scale based on D, with the pitches E F# G A B C#. Its key signature has two sharps: F# C#. Its Relative Minor scale is Bm Minor. Its Parallel Minor is D Minor.

"A Major" (or the key of A) is a major scale based on A, with the pitches A B C# D E F# G#. Its key signature has three sharps: F# C# G#. Its Relative Minor scale is F# Minor, Minor. Its Parallel Minor is A Minor.

"E Major" (or the key of E) is a major scale based on E, with the pitches E F# G# a B C# D#. Its key signature has four sharps: F# C# G# D#. Its Relative Minor scale is B Minor. Its Parallel Minor is E Minor.

"B Major" (or the key of B) is a major scale based on B, with the pitches C# D# E F# G# A#. Its key signature has five sharps: F# C# G# D# A#. Its Relative Minor scale is G# Minor. Its Parallel Minor is B Minor and, its enharmonic equivalent is Cb minor.

"F# Major" (or the key of F#) is a major scale based on F#, with the pitches F# G# A# B C# D# E#. Its key signature has six sharps: F# C# G# D# A# E#. Its Relative Minor scale is G# Minor. Its Parallel Minor is F# Minor and, its enharmonic equivalent is Gb minor.

"C# Major" (or the key of C#) is a major scale based on C#, with the pitches, all sharps C# D# ES F# G# A#. Its key signature has seven sharps: F# C# G# D# A# E# B#. Its Relative Minor scale is A# Minor. Its Parallel Minor is C# Minor, and its enharmonic equivalent is Db minor. C# is a somewhat easy key and scale to memorize as all the note are sharp.

"F# Major" (or the key of F#) is a major scale based on F#, with the pitches F# G# A# B C# D# E#. Its key signature has six sharps: F# C# G# D# A# E#. Its Relative Minor scale is G# Minor. Its Parallel Minor is F# Minor and, its enharmonic equivalent is Gb minor.

"Bb Major" (or the key of Bb) is a major scale based on Bb, with the pitches Bb C D Eb F G A. Its key signature has two flats: Bb Eb. Its Relative Minor scale is G Minor. Its Parallel Minor is Bb Minor. B-flat major is a suitable key for most wind instruments, especially those for which it is their home key, such as clarinets, trumpets, tenor saxophone, soprano saxophone and flutes in B-flat.

"Eb Major" (or the key of Eb) is a major scale based on Eb, with the pitches Eb F G Ab Bb C D. Its key signature has three flats: Bb Eb Ab. Its Relative Minor scale is C Minor. Its Parallel Minor is Eb Minor. E flat major is often associated with bold, heroic music, in part because of Beethoven's usage.

"Ab Major" (or the key of Ab) is a major scale based on Ab, with the pitches Ab Bb C D Eb F G. Its key signature has four flats: Bb Eb Ab Db. Its Relative Minor scale is F Minor. Its Parallel Minor is Ab Minor.

"Db Major" (or the key of Db) is a major scale based on Db, with the pitches Db Eb F Gb Ab Bb C. Its key signature has five flats: Bb Eb Ab Db Gb. Its Relative Minor scale is Bb Minor. Its Parallel Minor is Db Minor.

"Gb Major" (or the key of Gb) is a major scale based on Gb, with the pitches Gb Ab Bb Cb Db Eb Ab F. Its key signature has six flats: Bb Eb Ab Db Gb Cc. Its Relative Minor scale is Eb Minor. Its Parallel Minor is Gb Minor, usually replaced by F-sharp minor, since G flat minor, which would have nine flats, is theoretically possible but is not typically used.

"Cb Major" (or the key of Cb) is a major scale centered around Cb, with the following pitches: Cb, Db, Eb, Fb, Gb, Ab, and Bb. The key signature of Cb Major includes seven flats: Bb, Eb, Ab, Db, Gb, Cb, and Fb. The relative minor scale of Cb Major is Ab Minor, while the parallel minor is Cb Minor. Cb Major is considered relatively easy to memorize, as all of its notes are flat.
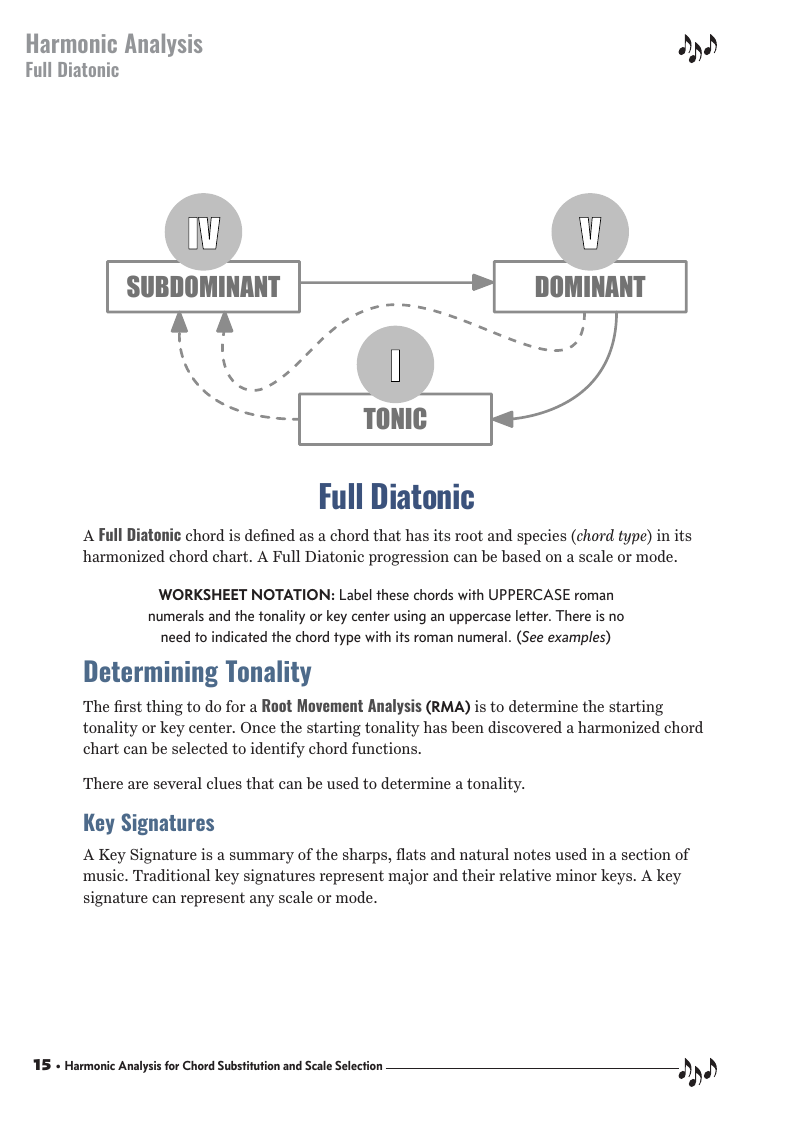
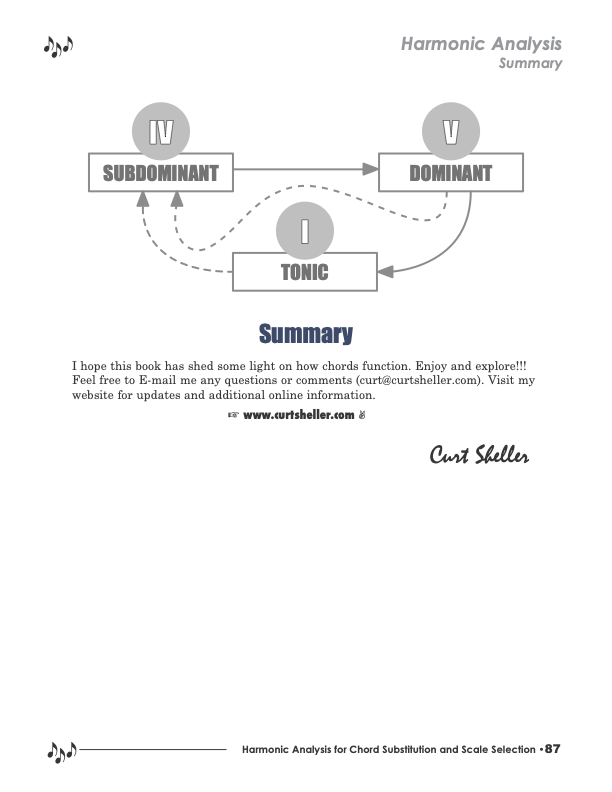
Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song, or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution. This lesson covers the Full Diatonic harmonic principle.
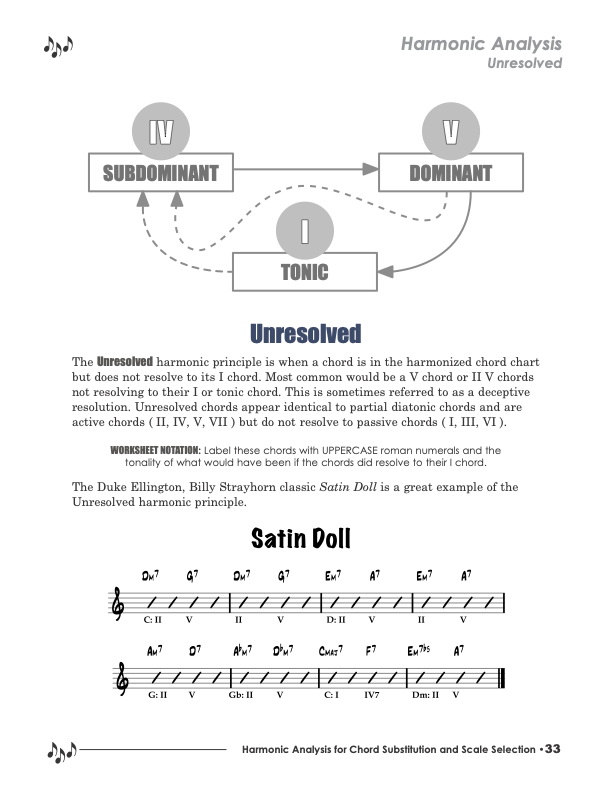
Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song, or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution. This lesson covers the Unresolved harmonic principle.
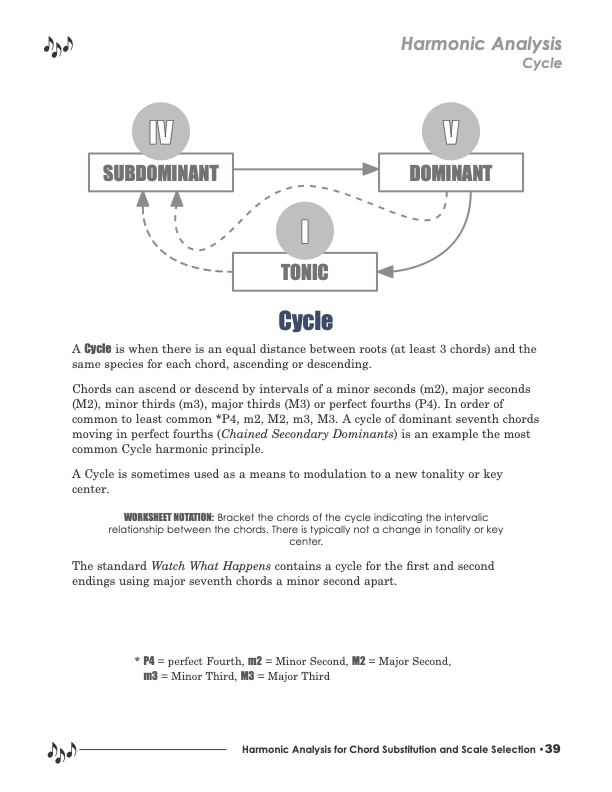
Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song, or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution. This lesson covers the Cycles harmonic principle.

Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song, or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution. This lesson covers the Internal Modulation harmonic principle.
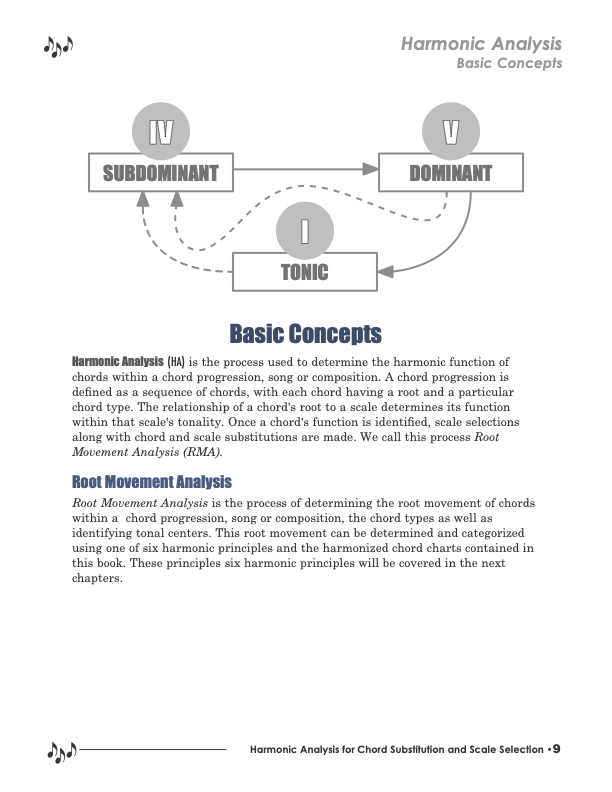
Harmonic Analysis is the process of determining the root movement of chords within a chord progression, the chord types that are used as well as identifying tonal centers. This root movement can be determined and categorized using one of six harmonic principles and the harmonized chord charts referenced in the lessons.
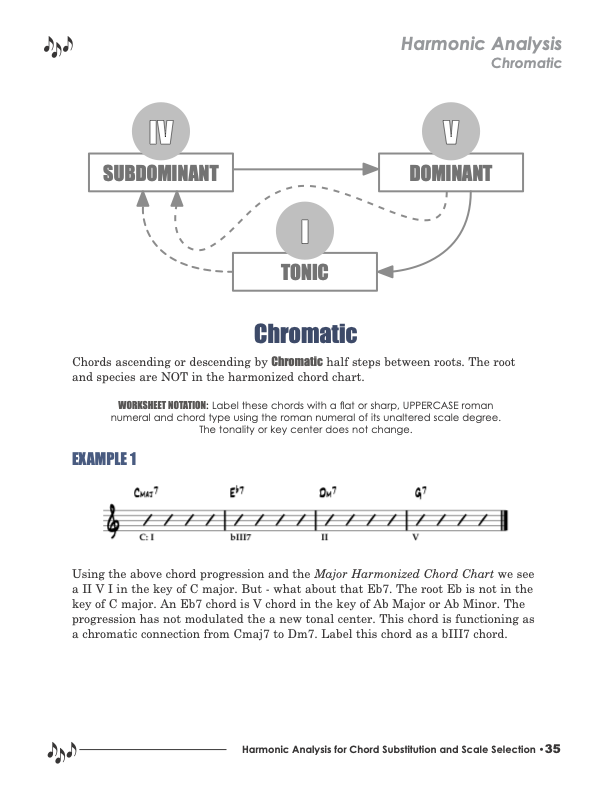
Harmonic Analysis is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song, or composition. This analysis is then used to make scale selections for improvisation and chord substitution. This lesson covers the Chromatic harmonic principle.

Major and Minor Harmonized Chord Charts are used for while doing a Harmonic Analysis (HA). Shows triads and 4-part chords for ALL 15 major and minor keys. "Yes, Virginia there are 15 keys."

"Harmonic Analysis" is the understanding of the functional sequence of chords. It is the process used to analyze the harmonic structure of a progression, song or composition. A blank worksheet and examples for notating your harmonic analysis.

A Harmonic Analysis is then used to make vertical and horizontal scale selection for improvisation and chord substitution.

Harmonic Analysis (HA) is the process used to determine the harmonic function of chords within a chord progression, sequence, composition or song. A chord progression is defined as a sequence of chords, each chord has a root and has a particular chord type.

Sometimes called the “learning key”, the key of C Major is one of the easiest keys to memorize and begin using. C major (often just C or key of C) is a musical major scale based on C, with pitches C D E F G A B C. Its key signature has no flats or sharps. Its relative minor is A minor A B C D E F G A B.

Called the "learning scale" for a reason. The major scale is a great scale for learning how music and chords work. It’s a core scale from which a majority of your core, essential scales can be derived. There are 15 major scales.

The distance between any two notes can be defined by steps - half steps, whole steps, semi-tones, whole tones. From this series of steps you can get the names of the notes of ANY of the fifteen major scales.

The only scale in music with ALL twelve notes of one octave. Not much use for improvisation or solos – but a great scale for learning the notes of the ukulele fingerboard, figuring out scales, chords and more...
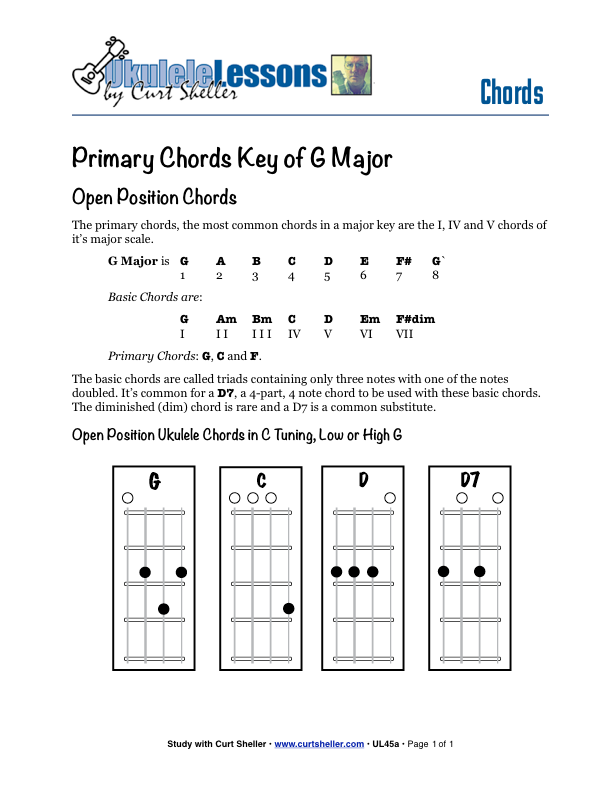
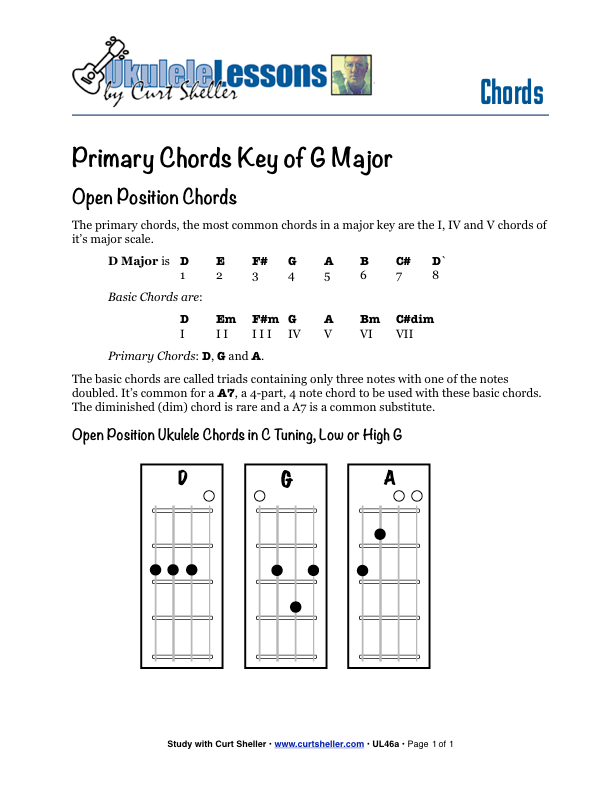
The primary chords for any major key are the I, IV, and V chords of its corresponding major scale. For G Major the primary chords are: G, C, D, and D7.

Common chord progressions for the key of G. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of G.

Common chord progressions for the key of A. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of A.

Common chord progressions for the key of E. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of E.

Common chord progressions for the key of B. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of B.

Common chord progressions for the key of F#. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of F#.

Common chord progressions for the key of C#. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of C#.

Common chord progressions for the key of F. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of F.

Common chord progressions for the key of Bb. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of Bb.

Common chord progressions for the key of Eb. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of Eb.

Common chord progressions for the key of Ab. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of Ab.

Common chord progressions for the key of Db. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of Db.

Common chord progressions for the key of Gb. Using the primary and seconday chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of Gb.

Using the primary and secondary chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of Cb. The key of Cb is a pretty rare key but actually an easy key to relate to the key of C. The key of C has ALL natural notes and the key of Cb has all flat notes for the scale: Cb Db Eb Fb Gb Ab Bb Cb`. The names of the notes are the easy part, the chords are typically played as movable form chords with only the Fb ( the enharmonic equivalent name is E ) available as an open string in the C tuning.
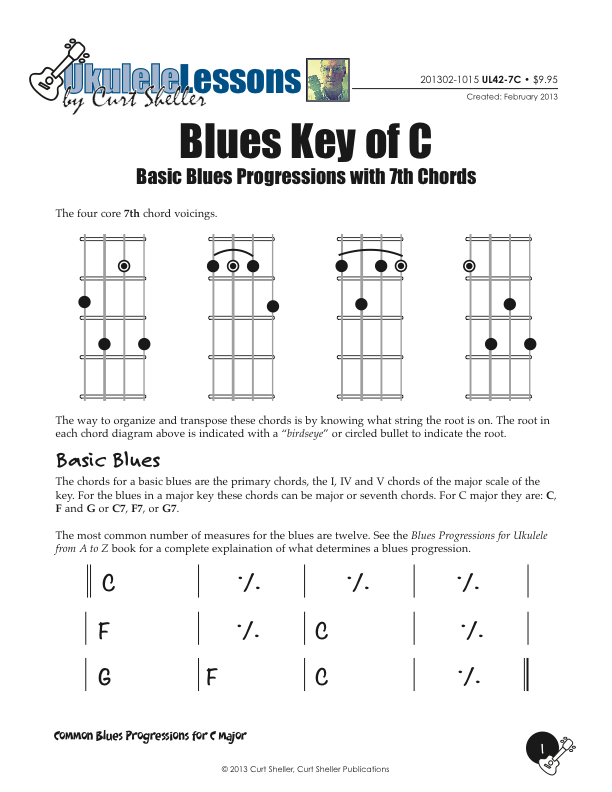
Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of C major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is a great way to explore this core chord in various keys. These are the two most common blues progressions used in traditional and contemporary music.
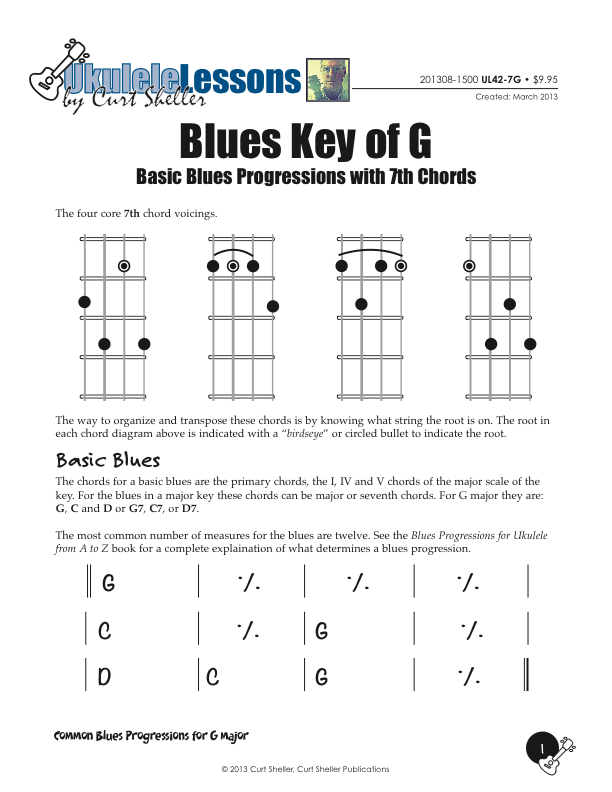
Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of G major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys. These are the two most common blues progressions used in traditional and contemporary music.
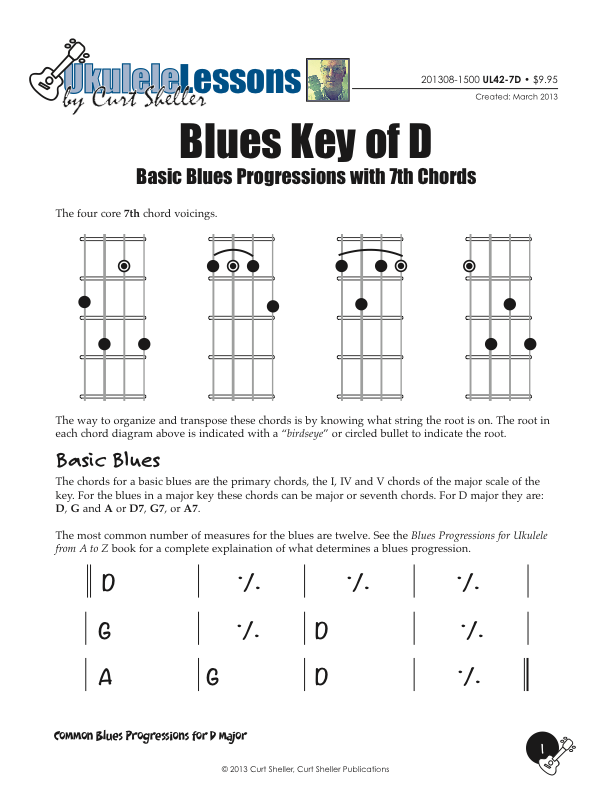
Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of D major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.
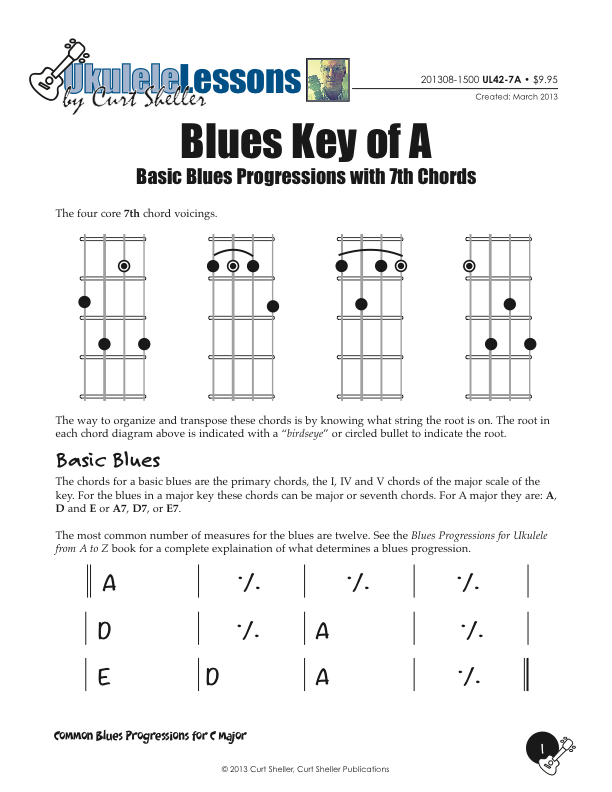
Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of A major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.
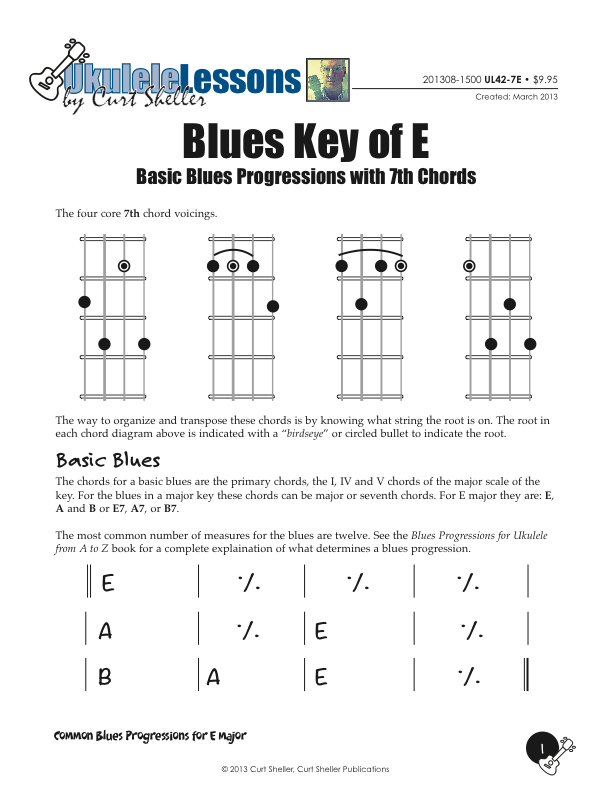
Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of E major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.
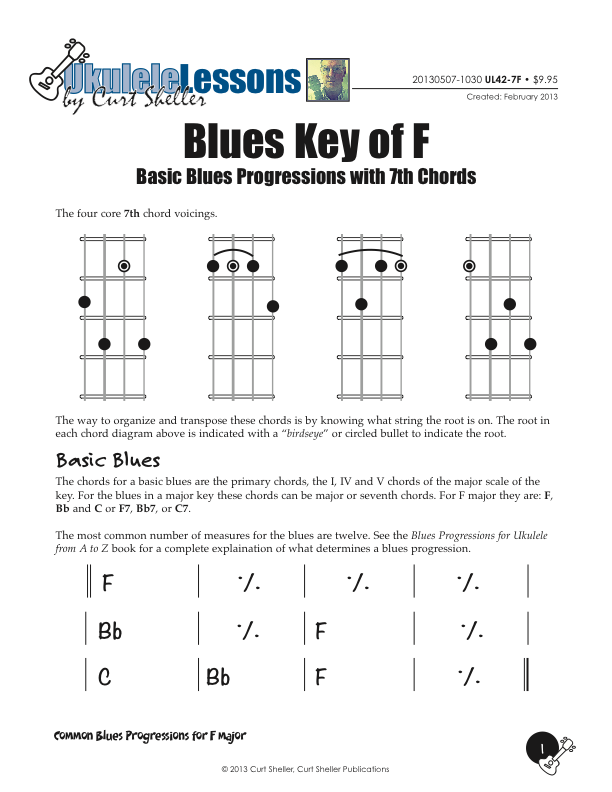
Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of F major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.

Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of Bb major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.

Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of Eb major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.

Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of Ab major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys.

Basic and Quick Change blues chord progressions in the key of Db major using the core 7th chords from the Big Six series of lessons. This is great way to explore this core chord in various keys

Common chord progressions for the key of D. Using the primary and secondary chords for the key explore these common chord progressions for the key of D. D is one of the common keys that include C, G, *D, A, and E.
The primary chords for any major key are the I, IV, and V chords of its corresponding major scale. For D Major, the primary chords are: D, G, A, and A7. From the primary and secondary chords of a major key, countless songs and chords progressions can be played.
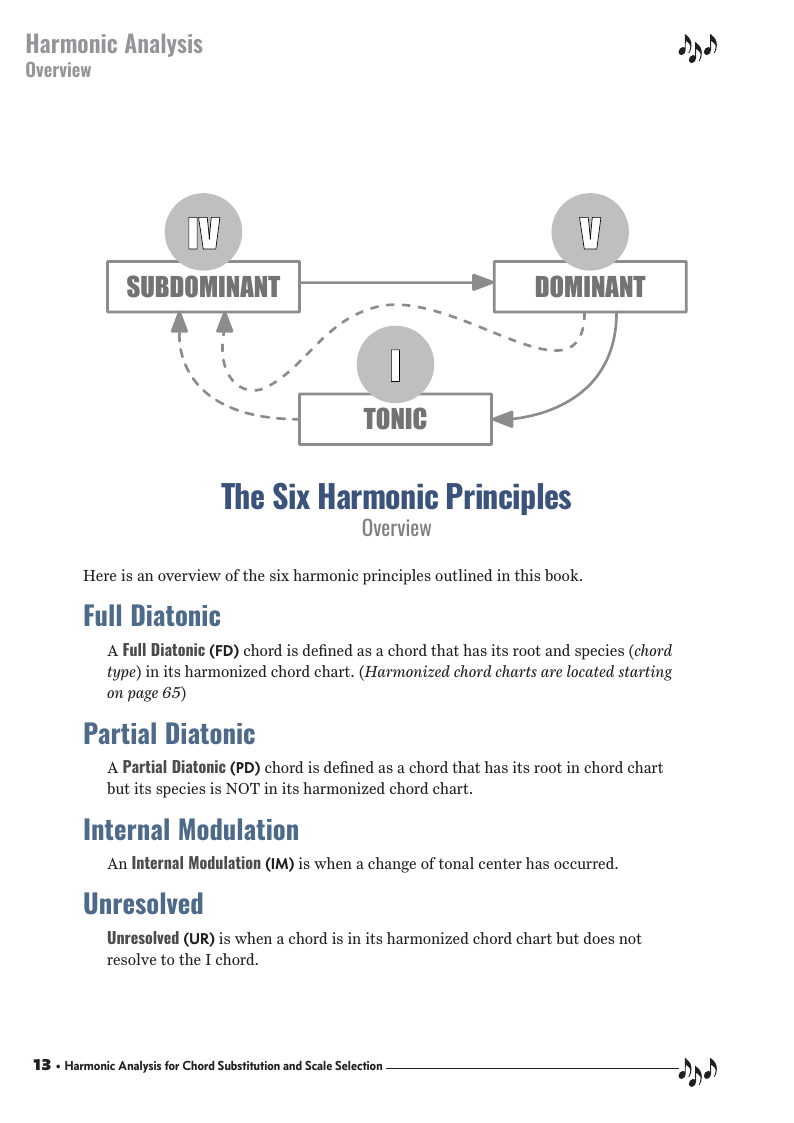
This lessons cover the "Six Harmonic Principles" that are used to do a Harmonic Anlyasis - the understanding of the functional sequence of chords.
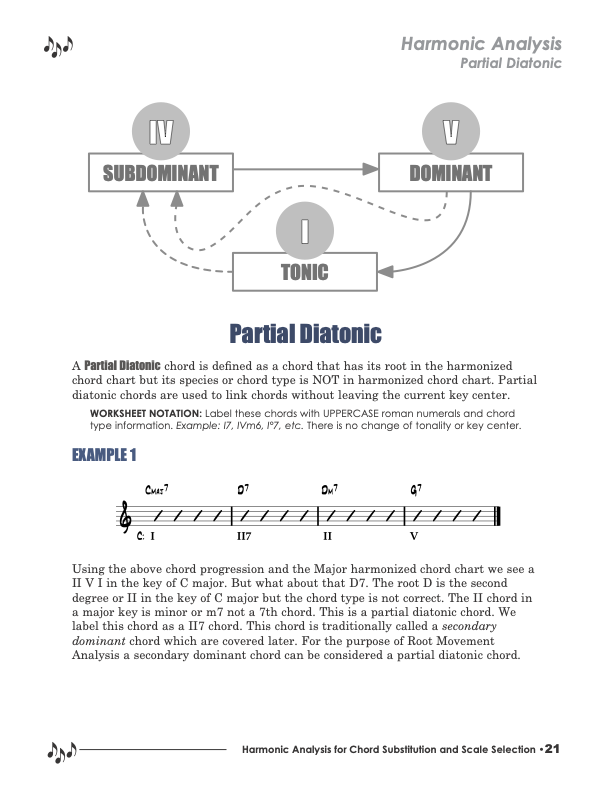
"Partial Diatonic" is defined as a chord that HAS its root in the - "Harmonize Chord Chart," but its species or chord type is NOT in the Harmonized Chord Chart. Partial Diatonic chords are used to link chords without leaving the current key center. Secondary Dominant chords are a big part of this harmonic principle.
Common chord progression are simply the sequence of chords that contiounly show up in various styles of music and common keys.
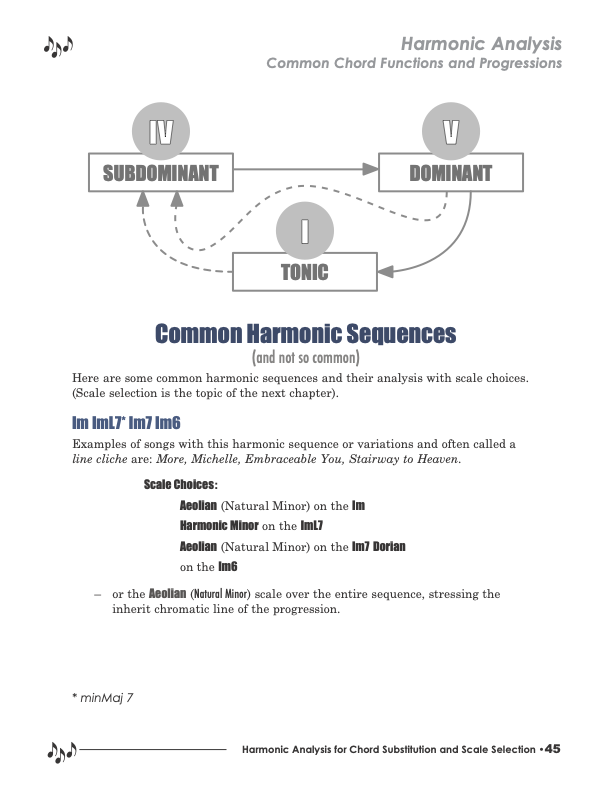
Common harmonic sequences and their analysis with scale choices.

Harmonic Analysis ( HA ) is the process used to determine the harmonic function of chords within a chord progression. A chord progression is defined as a sequence of chords, each chord has a root and has a particular chord type. The relationship of a chord's root to a scale determines its function within that scale's tonality. Once a chord's function is identified, scale selections along with chord and scale substitutions can be made. This process is called Root Movement Analysis ( RMA ). This series of lessons are extracted from my book for use with individual private and on-line students. Each lesson directly corresponds the chapters in my book Harmonic Analysis for Scale Selection and Chord Substitution by Curt Sheller (me).
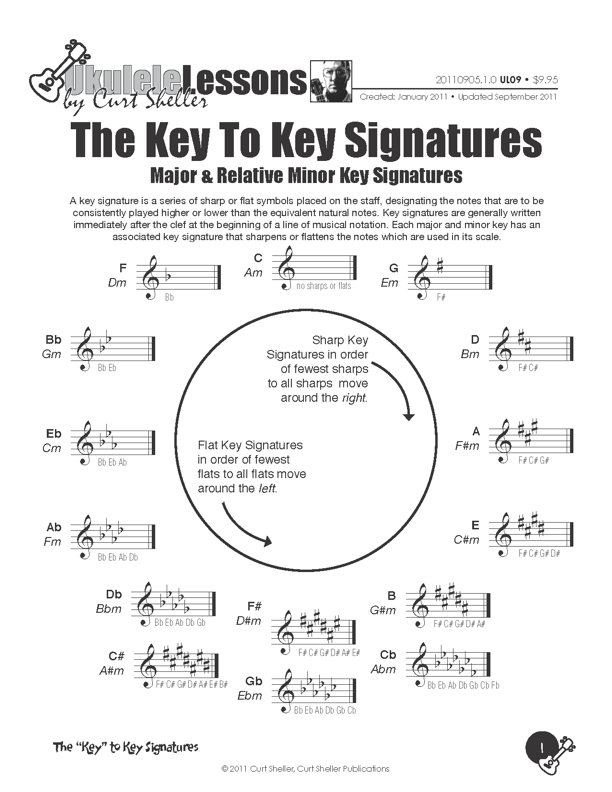
A "Key Signature" is a series of sharp or flat symbols placed on the staff, designating the notes that are to be consistently played higher or lower than the equivalent natural notes. Key signatures are generally written immediately after the clef at the beginning of a line of musical notation. Each major and minor key has an associated key signature that sharpens or flattens the notes which are used in its scale.
HARMONIC ANALYSIS for Scale Selection and Chord Substitution explored the six harmonic principles for analyzing chord progressions and songs using tradition tonic-dominant harmony and the scale modes.

The ultimate goal for any musician when playing a musical instrument is to "Play by Ear". It’s true whether you’re singing, banging a drum, strumming a guitar, or our favorite instrument, the ukulele. If your fingers can already interpret and follow what your inner ear commands, you’ve obtained your goal and are "Playing by Ear."

Listening to songs and wanting to play the same songs on ukulele – that's what draws most people to the ukulele. That and it looks like a load of fun and easy to play – which it is. Then you need to actually remember the songs that you're learning, so you can play them again. And, hopefully, not have to read them off a sheet all the time.

A key signature is a summary of the sharps or flats in a Major or its relative Natural Minor scale. Key signatures are generally written immediately after the clef at the beginning of a line of standard musical notation. Each major and minor key has an associated key signature that sharpens or flattens the notes which are used in its scale.

The "Andalusian" cadence is a term adopted from flamenco music for a chord progression comprising four chords descending stepwise. It is otherwise known as the minor descending tetrachord. Traceable back to the Renaissance, its effective sonorities made it one of the most popular progressions in classical music.

In jazz and jazz harmony, the chord progression from IV7 to bVII7 to I has been nicknamed the backdoor progression or the backdoor II-V. This name derives from an assumption that the normal progression to the tonic, the II-V-I turnaround (II-V7 to I, see also authentic cadence) is, by inference, the front door. It can be considered a minor plagal cadence in traditional theory.

The twelve bar blues and its many variants use an elongated, three-line form of the I - IV - V chord progression that has also generated countless hit records, including the most significant output of rock and rollers such as Chuck Berry and Little Richard.
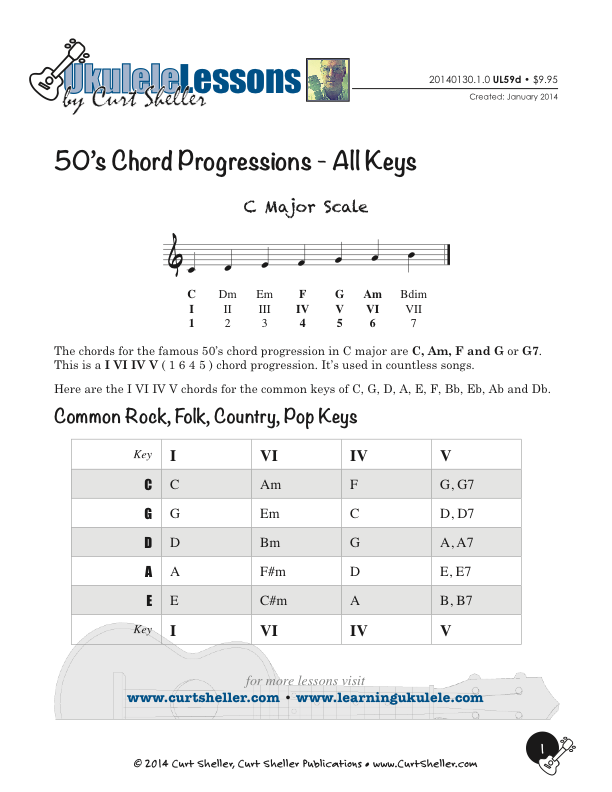
Another common way of extending the I - IV - V sequence is by adding the chord of the sixth scale degree, giving the sequence I - vi - IV - V or I - vi - ii - V, sometimes called the 50s progression.

Diatonic scales such as the major and minor scales lend themselves particularly well to the construction of common chords because they contain a large number of perfect fifths. Such scales predominate in those regions where harmony is an essential part of music, as, for example, in the common practice period of western classical music.

Three-chord tunes, though, are more common, since a melody may then dwell on any note of the scale. Often the chords may be selected to fit a pre-conceived melody, but just as often it is the progression itself that gives rise to the melody.

The most important notes or chord tones in a chord are the notes that contribute most to the actual sound or “color” of the chord. For a major or minor triad, the third of the chord performs this function. For other chords, any note that makes it different from other chord types with the same root are the color tones.
This lesson is a more for less type of lesson exploring what notes are actually important in chords. The best place to start with this concept is 4-part chords and the Big Six Core Chords.

"Free Form" chords are those chords that do not fall into one of the other chord categories. They typically don't show up in chord dictionaries or software programs.

A chord's name is comprised of it's letter name, either A, B, C, D, E, F, or G and it's type information symbols which encapsulates the instructions for building a chord.
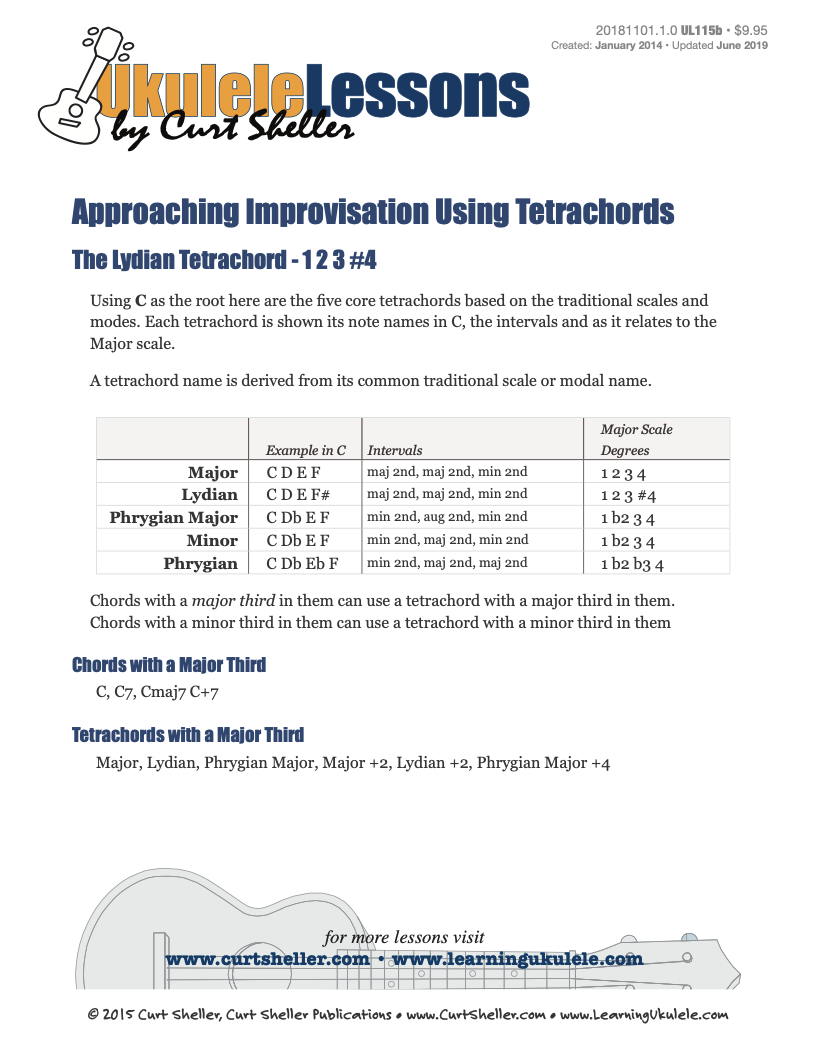
The Lydian tetrachord is the 1 2 3 #4 of a Lydian, Lydian Dominant, or Whole Tone scale.

The Phrygian Major tetrachord is the 1 b2 3 4 of a Phrygian scale.

In the key of C major Pachelbel's Canon is: C G Am Em F C F G. This is a I V VI III IV I IV V in harmonic analysis notation. In Nashville Numbering it's 1 5 6 3 4 1 4 5. It is a full diatonic progression with all the chords coming from it's parent major scale. A bit of a varaition of the Four Chord Pop progression.
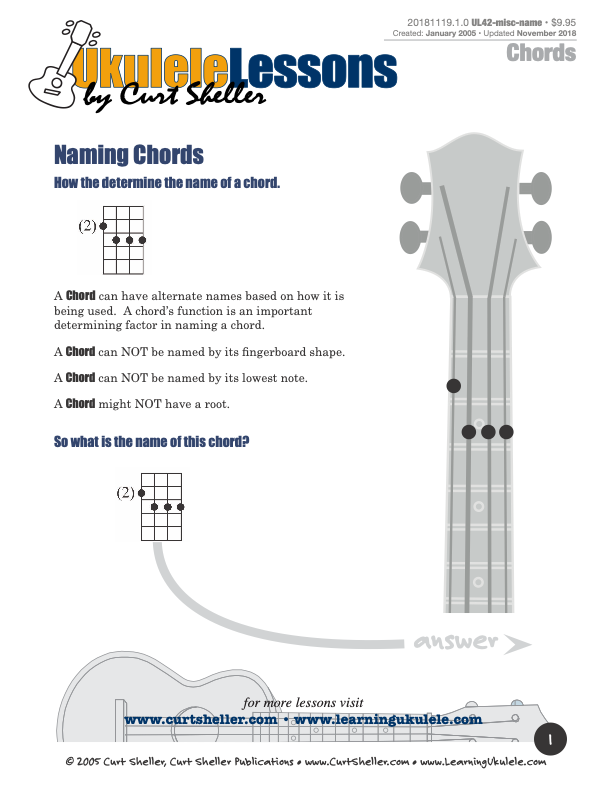
A Chord can have alternate names based on how it is being used. A chord's function is an important determining factor in naming a chord. So unless you know the harmonic function of a given chord, you might not be able to accurately name it.

This lesson presents the traditional approach for learning the chord tones of chords with a little twist to make it a bit easier. A Chord is three or more notes sounded simultaneously - together or almost together. The minimum number of notes required for a chord are three. These three note chords are called triads. Two notes are usually referred to as an interval or dyad. Each note of a chord is called a chord tone.

An interval is the distance between two notes. An interval has a name and a type. Intervals can be played one note (melodic) or two notes (harmonic) at a time, ascending or descending. Simple and Compound Intervals are taken from a major scale. Chromatic Intervals are NOT taken from a major scale. They are derived from the diatonic intervals.

A "Secondary Dominant" chord is defined as any seventh chord built on a scale root that is diatonic to the key that resolves up a perfect fourth or down a perfect fifth to a full diatonic chord. These chords function as a dominant (V) chord to the next chord, serving to temporarily tonicize the following chord.

Fred Flintstone is the main character of the animated sitcom The Flintstones, which aired during prime-time on ABC during the original series' run from 1960 to 1966. Fred is the husband of Wilma Flintstone and father of Pebbles Flintstone. His best friend is his next door neighbor, Barney, who has a wife named Betty and an adopted son, named Bamm-Bamm.

A metronome is a device that produces an audible click or other sound at a regular interval that can be set by the user, typically in beats per minute (bpm).




.jpg)